WORKING PRINCIPLE
HOW DOES OUR DP SERIES OF AIR OPERATED DOUBLE DIAPHRAGM PUMPS WORK?
Air Operated Double Diaphragm Pump is a special type of pneumatic displacement pump, that utilize a pressure differential in the air chambers to alternately creat suction and positive fluid pressure in the fluid chambers. Valve checks ensure a positive flow of fluid. Pump cycling will begin as air pressure is applied, and it will continue to pump and keep up with the demand. It will buid and mainain line pressure and will stop cycling once the maximum line pressure is reached and will resume pumping as needed.
The following is working principle of NUODEAN's DP Series of Air Operated Double Diaphragm pumps:
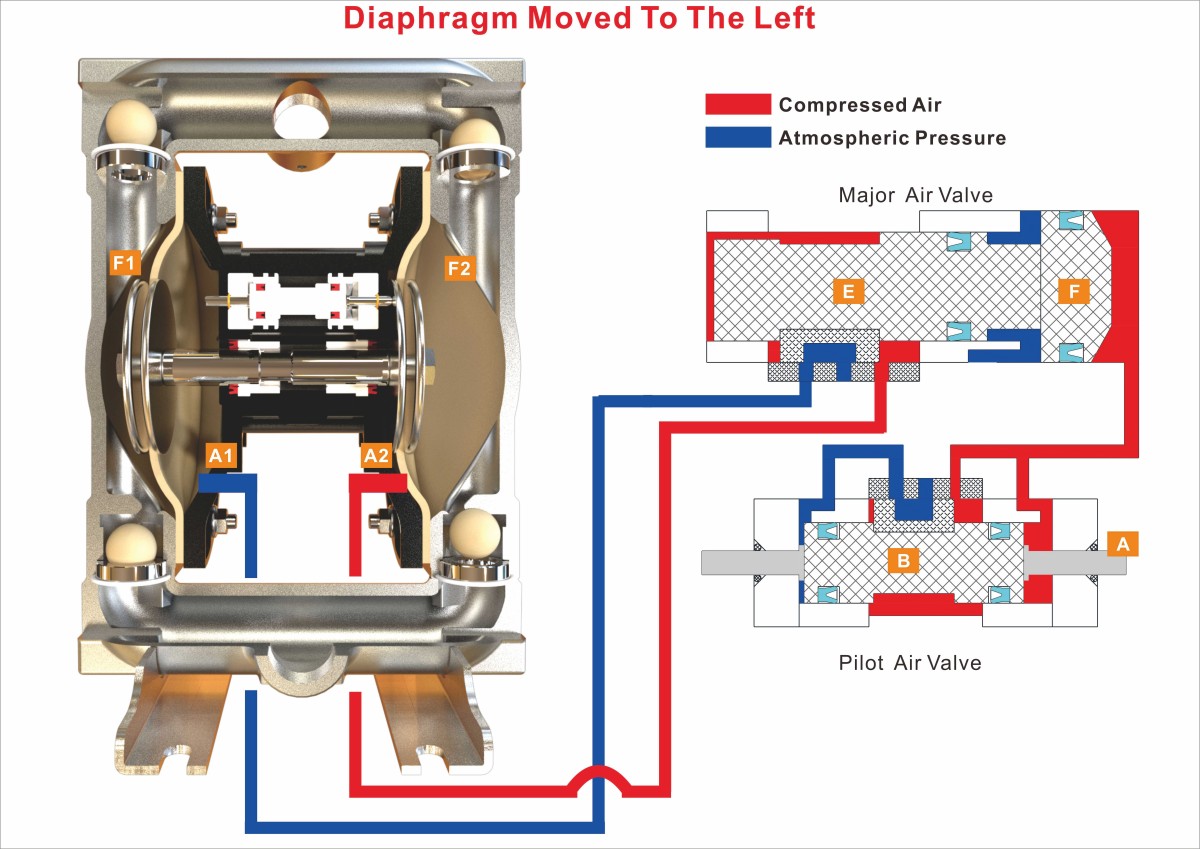
Diaphragm Moved From The Right To The Left
1. The diaphragm pushes the right Actuator Pin(A) mechanically moving the spool (B) to the left.
2. Compressed air flows to the right end of pilot air valve, pneumatically moving the spool (B) to the position shown.
3. Compressed air also flows to the large end (right end) of the Major Air Valve, acting on the right side of piston (F) to push piston (F) & spool (E) to the left and holds them in position because the area of the right side of piston (F) is bigger than the left side of spool (E).
4. When the diaphragms arrives at the left end of the stroke, the left air chamber A1 of the pump is connected to the exhaust port through the Major Air Valve. Then the air pressure in the left air chamber A1 is discharged. At the same time, the right air chamber A2 of the pump is connected with compressed air through the Major Air Valve, and then is filled with the compressed air quickly.
5. The compressed air in the right air chamber A2 of the pump pushes the diaphragms to start moving to the right.
6. The left liquid chamber F1 of the pump start to become larger due to the diaphragms’ moving to the right,then start to suck in the liquid from the inlet of the pump; At the same time, the volume of the right liquid chamber F2 of the pump start to decrease, and then the liquid in the right liquid chamber F2 starts to be pumped to the outlet of the pump.
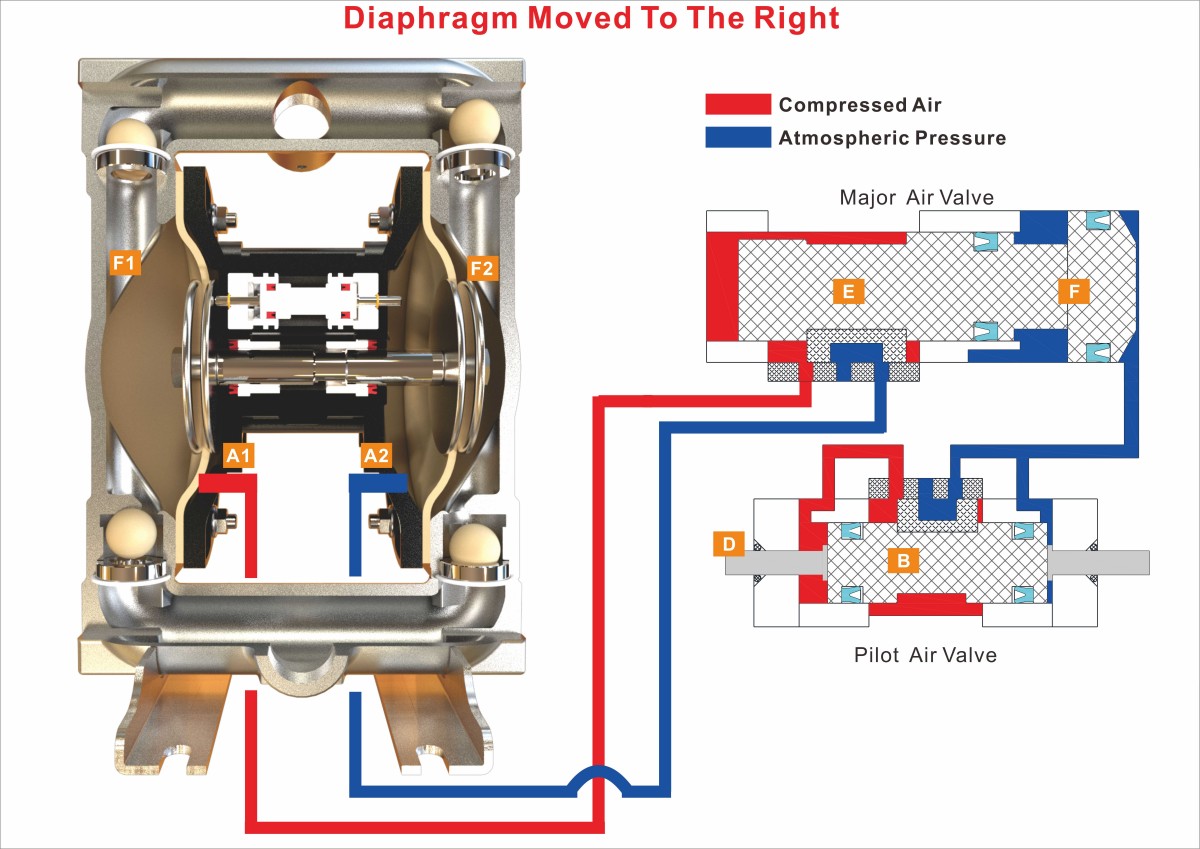
Diaphragm Moved From The Left To The Right
1. The diaphragm pushes the left Actuator Pin (D) mechanically moving the spool (B) to the right.
2. Compressed air flows to the left end of pilot air valve, pneumatically moving the spool (B) to the position shown.
3. Constant compressed air supply acting on the left side of the spool (E), shifts the piston (F) & spool (E) to the right and holds them in position because the compressed air in the right end of the Major Air Valve is exhausted.
4. When the diaphragms arrives at the right end of the stroke, the right air chamber A2 of the pump is connected to the exhaust port through the Major Air Valve. Then the air pressure in the right air chamber A2 is discharged. At the same time, the left air chamber A1 of the pump is connected with compressed air through the Major Air Valve, and then is filled with the compressed air quickly.
5. The compressed air in the left air chamber A1 of the pump pushes the diaphragms to start moving to the left.
6. The right liquid chamber F2 of the pump start to become larger due to the diaphragms’ moving to the left, then start to suck in the liquid from the inlet of the pump; At the same time, the volume of the left liquid chamber F1 of the pump start to decrease, and then the liquid in the left liquid chamber F1 starts to be pumped to the outlet of the pump.

